The History of Ålesund
- 1 Comment
- by Emma
The History of Ålesund
Ålesund is today famous for its famous art nouveau architecture, but the city has a fascinating past all the way back to the time of the Vikings. The settlement at Ålesund didn’t emerge until the 18th century, but the area around Ålesund is mentioned in all the Norse sagas as a wealthy trading area. After Ålesund got market rights to compete against Bergen’s monopoly, people began settling here to take part in the rich cod fisheries. A fire in 1904 completely devastated the city, but Ålesund rose from the ashes as one of the most beautiful cities in Norway. Here is my overview of the history of Ålesund.
In this article...
The Viking Sagas
Ålesund isn’t mentioned for the first time until the 18th century, but places around Ålesund are known from the Viking Age. For example, Steinvåg is mentioned in connection with St. Olav’s visit in 1029, and in 1184 King Sverre (who founded Trondheim) visited the area.
However, there is one place in particular that is famous from the Viking Age.
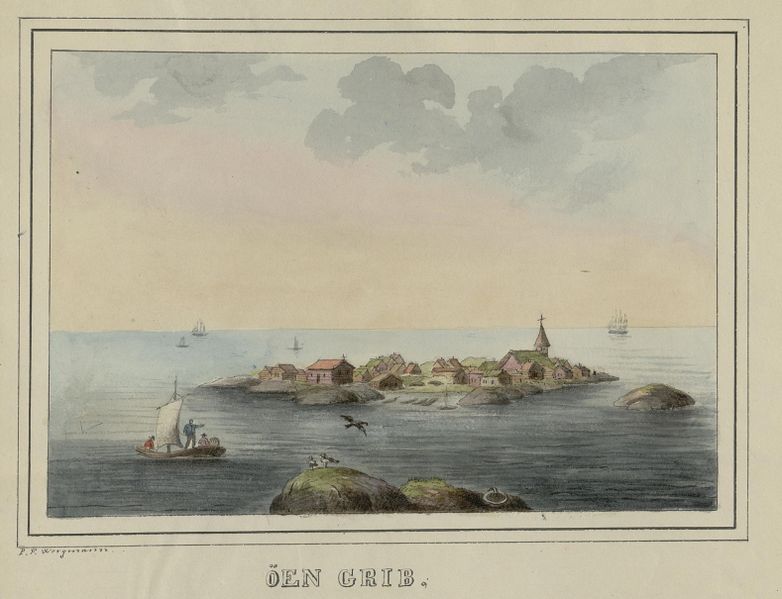
Borgund
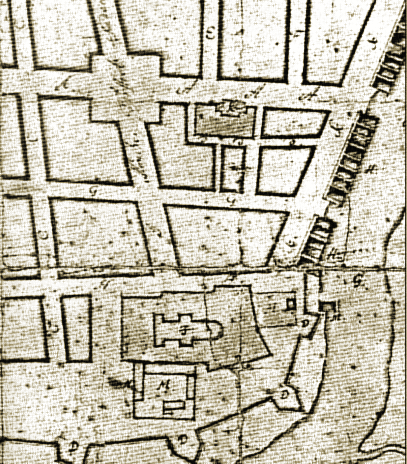
To the southeast of Ålesund city centre is a place known as Borgund (not to be confused with the famous stave church of the same name). Borgund is the oldest known dwelling in the region. This is where the history of Ålesund begins.
Archaeological excavations have shown settlement from the 11th century onwards. The remains of up to four marble churches have been found, indicating the area was very wealthy and important. One of the medieval churches, Borgund Church, is still standing today. Excavations show there there 40-50 dwellings here.
The reason for Borgund’s importance was the rich fisheries in the Borgund Fjord, in particular the cod fisheries. The town functioned as a gathering and distribution centre for products from the region that would then be sent on to Bergen and sold to the Hanseatic League. Exchange goods, such as ceramics from Germany and textiles from England, were brought back from Bergen.
Borgund survived partly in thanks to a powerful family called the Giske Family.
Visiting Borgund Today: Borgund is located just outside of Ålesund. You can visit the church or one of two museums on the side; The Medieval Museum (https://www.vitimusea.no/musea/middelaldermuseet) or the Sunnmøre Museum (https://www.vitimusea.no/musea/sunnmoere-museum)
You can read about the excavation work on the University of Bergen website (including pictures): https://www.uib.no/en/rg/borgund-kaupang/134757/excavating-borgund
Giske
The Giske Family was a Norwegian aristocratic family from the Viking Age through to the 17th century. They lived on an island called Giske, which is today just north of the city of Ålesund and accessible by road tunnel.
The family is mentioned in the Norse Sagas and were connected to both St. Olav and the King Harald Hardråde through marriage. One of the Giske’s fell at the famous Battle of Stamford Bridge in 1066, which is regarded as the end of the VIking Age.
Through marriage and purchasing, the Giske family became one of the wealthiest families in Norway. The last Giske died in 1605 (a widow with no children), and at the time the estate owned 192 properties.
It is possible to visit the island of Giske today. Their church, Giske Church, still stands today. Burial mounds are also located on the island and can be visited.
Ålesund's Early Years
Due to Bergen’s monopoly on trade in Norway, Borgund eventually declined in importance. However, Bergen’s monopoly did not last forever; starting in the 1700s there was increased demand to open more market towns along the Norwegian coast. The site of present-day Ålesund was chosen was one of these new market towns. There were people living here at the time; Ålesund was first mentioned in 1766, when a Norwegian priest called Hans Strom mentioned Aalesund (the old spelling of the town name).
Ålesund received trading rights in 1793. However, this did not immediately result in success; it took another 60 years before major growth started. Full market town rights were granted in 1848, and after that the city began to see growth.
Ålesund’s town centre was built around the narrow Ålesundet sound between the islands. The first settlers came from Bergen; living and trading here for part of the year.
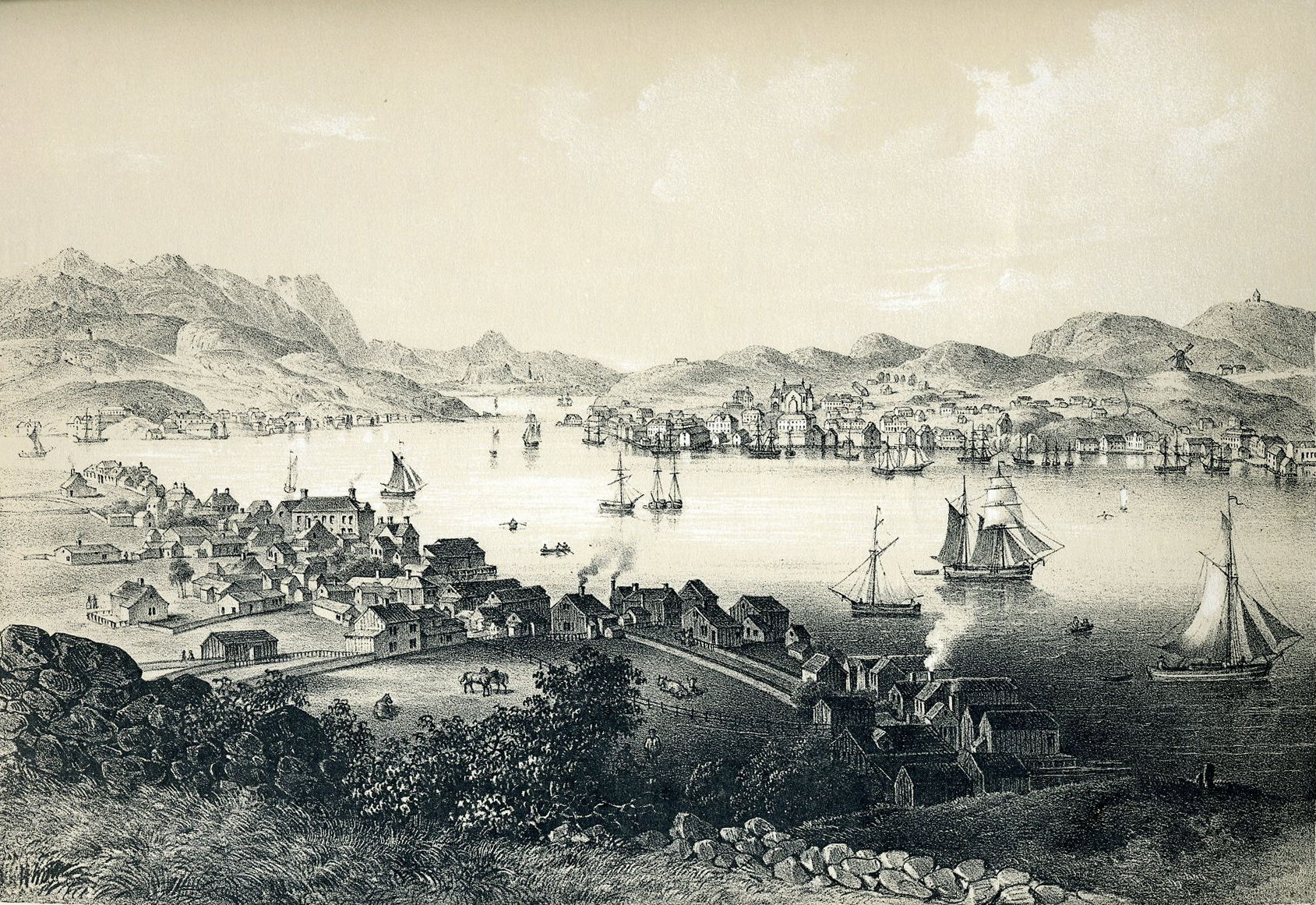
Rapid Growth & Wealth
The modern founders of the town are considered to be the member of Parliament, Peter Tonning, and the fish exporter Carl Rønneberg. They ensured that Ålesund was given rights to trade and export without going through Bergen. Because of this, Ålesunds growth coincides with Bergen’s decline.
Thanks to the natural harbour, Ålesund grew very quickly. The nearby rich fisheries and the harbour brought people from all over the west. Eventually fish processing factories were established, and the expanding fishing fleet grew here as well. Eventually steamships began docking at Ålesund and larger factories were built.
In 1872, author Magdalene Thoresen described the city as follows:
It is a fresh sight to see this small coastal town with its newly built houses, scattered over the bare mounds that often look like reefs, and you get the impression that it was built in a hurry, built up by chance and the mood which comes with a fast, dangerous profession. Here, no even, calm deliberation goes through anything; even the large, dizzying warehouses and individual magnificent buildings speak only of the rapid rise of profit and the boldness of large speculations. Of course, there are also buildings which clearly show that here prosperity resides in safe enclosure, here no more daring. But most of it gives the impression of rapid rise
Ålesund continued to experience wealth and rapid growth until the fire of 1904 struck.

1904 Fire
Because of the rapid growth of the city, the towns buildings were somewhat randomly built timber buildings. This was a huge reason why the city was so quickly devastated by fire.
On the 23rd of January 1904, a fire started in the Aalesund Preserving Company’s factory at around the same time a storm from the southwest was blowing through. Overnight, the fire destroyed over 800 buildings and 10,000 of Ålesund’s 12,000 people were left homeless.
Only one person died; an elderly woman who had safely evacuated her home but decided to go back to retrieve her purse. Ironically, she lived closest to the fire station.
One other man refused to leave his home so his friends and family carried out all his furniture and belongings to save them from the fire. After the fire, the house survived but all the furniture was destroyed.
Financial Help
The news of the destruction of Ålesund spread all throughout Europe, and money began pouring in to help rebuild the city. One of the biggest contributors was Kaiser Wilhelm II, who had spent many vacations in the area. He sent five support ships full of food, medicine, construction materials, blankets, and other forms of aid to the town. The main street in Ålesund is named after him because of this.
Architectural Style
After the fire, the city decided to employ fresh Norwegian architects to design and rebuild the town. The approximately 50 architects selected to design the town had just studied abroad and become influenced by the Jugendstil, or Art Nouveau, style, and decided to rebuild the town in a very uniform style.
Art Nouveau in Norway takes a lot of influence from medieval buildings such as stave churches but also motifs from the Viking Age and Norse Sagas. Additionally, lots of nature elements are used on the buildings.
Learn more: In Ålesund you’ll find the Jugendstilsenteret, a museum all about Ålesund’s art nouveau architecture. The museum also covers how the city was devastated by fire but quickly rebuilt itself.
Rebuilding
Ålesund was rebuilt very quickly. By 1906, a major part of the town had been rebuilt with well-planned streets and strict building specifications. Timber was forbidden in the town centre but still exists around the town.
The big reason for the rapid rebuilding was that there were so many tradesmen without work at the time, so it was easy to hire people.
World War II
After the Nazi invasion of Norway on the 9th of April 1940, Ålesund was not immediately occupied. It was free territory during the initial phase of fighting in Norway. The government used the Ålesund coastal radio station to communicate with the United Kingdom, and because of this Ålesund was bombed in late April 1940.
After the Nazis occupied Ålesund, the mountain Aksla was used for military fortifications.
Ålesund became known as ‘Little London’ by the Gestapo because of the resistance work that took place here. The large transport group known as the Shetland Bus used Ålesund as one of their major bases for transporting goods between Shetland and Norway. Several members of the group were caught and executed for their participation in the group.
Ålesund Today
Today Ålesund is one of the main centres in Western Norway and is also home to Norway’s largest and most modern ocean-going fishing fleets. There are also shipyards, mechanical workshops and other industries here.
You can read about Ålesund, as well as what to do when visiting, on my Ålesund travel guide page.